Salaried Class Taxation In USA
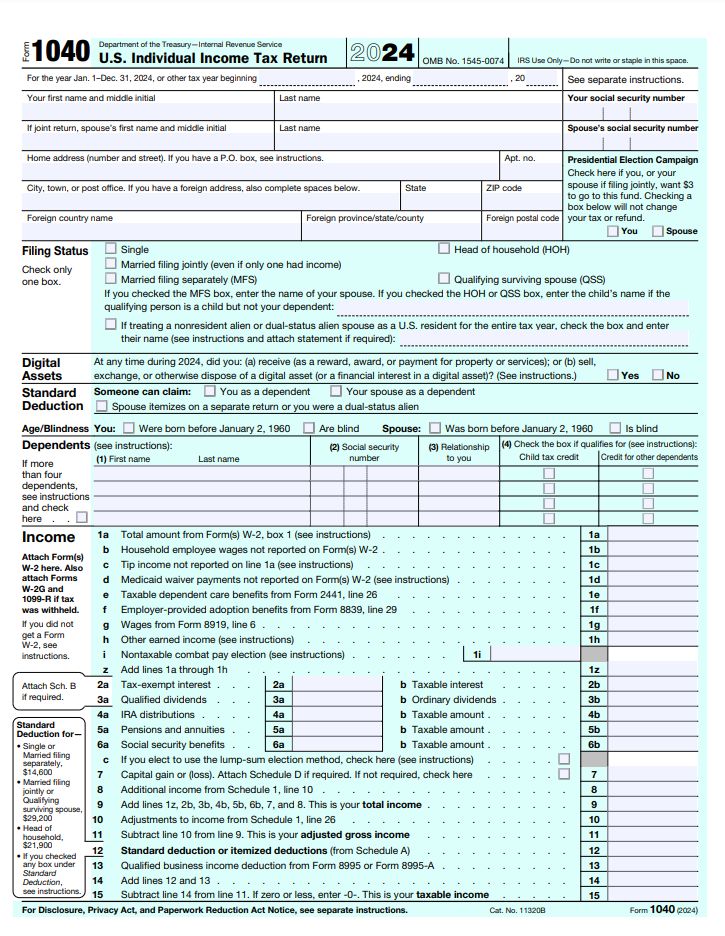
US Federal income tax is applied on income of salaried individuals based on gross income less allowable deductions. The tax is initially collected as withholding from employees and deposited with the IRS by the employers each month.
In computing the taxable income there are 2 types of deductions that are allowed to the employees.
“Above the Line deductions” i-e Gross income less certain specified deductions to reach at Adjusted Gross income (AGI) and “Below the line deductions” i-e AGI less standard deductions/itemized deductions.
1. Health savings account contributions (HAS): Contributions to HSA is deductible if individual is eligible
2. Commuting expenses: Specifically for those employees who need to carry tools or equipment to the work place & incurred additional commuting cost for transportation. This additional cost is deductible.
3. Automobile expenses: Expense incurred on Personal vehicle used for business purposes are deductible. There are 2 ways to calculate the deduction amount.
a) Actual basis: Actual expenses on running & maintaining the vehicle attributable to business use
b) Mileage rate: IRS publishes a standard business mileage rate each year for business miles driven. Normally this method is used. (67cents per mile for TY 2024)
4. Travel expense: Reasonable and necessary travel expenses are deductible for business purposes. The primary intention of travel must be business. Meals are 50% deductible while on business travel. (very detailed rules available for interested people).
5. Foreign travel: Not deductible unless it is purely for business purposes.
6. Entertainment, meals and business gifts: 50% deductible subject to certain conditions and restrictions
7. Home office expense: Subject to certain conditions these expense are deductible. In case of employees, it must be demonstrated that home office use is for the convenience of employer
8. Dues and subscriptions: Dues and other payments to labor unions, trade associations and professional organizations are fully deductible.
9. Education expenses: These are deductible subject to certain conditions and restrictions.
10. Interest on education loans: Interest paid on qualified education loans is deductible
Above all are itemized deductions and employee has option either to claim total of itemized deductions or standard deductions whichever is more beneficial. Standard deduction amounts are adjusted each year for inflation & vary based on the filing status of the taxpayer. For 2024, the following are standard deduction amounts
Single: $14,600
Married Filing Jointly: $29,200
Married Filing Separately: $14,600
Head of Household: $21,900
Above is a basic idea about deductions available to salaried/self employed persons and list is not exhaustive, may be more or less depending on case to case basis.